Residency programs provide essential clinical training for graduates who aim to advance their careers in specialized areas of pharmacy practice. They are pivotal if you're seeking roles in hospital, academic, or specialized pharmacy environments.
These programs, from Postgraduate Year One (PGY1) to more advanced specialties in PGY2, offer in-depth, hands-on experience that enhances clinical skills, expands career opportunities, and opens doors to valuable networking within the profession.1 We'll explore the types of pharmacy residency programs, the benefits they provide, and what you need to know to navigate the residency application process successfully.
Pharmacy Residency Program Requirements
Pharmacy residency programs provide extensive training across various clinical and administrative settings, often within hospitals or healthcare systems. They generally begin with a PGY1, which offers broad foundational training in patient care and may continue to PGY2, where you focus on a specialty area such as oncology, critical care, or pediatrics. Each program requires a Doctor of Pharmacy degree and often seeks candidates with strong clinical skills and a demonstrated commitment to patient care.2
For pharmacists interested in expanding their expertise, postgraduate options, including fellowships and dual residencies, offer alternative paths that emphasize research or advanced specialty training, further diversifying career possibilities.
Types of Pharmacy Residency Programs
Pharmacy residencies are typically divided into PGY1 and PGY2 programs, each with a specific focus and purpose.
PGY1 provides general training in areas such as internal medicine, emergency care, and community pharmacy. This initial year emphasizes patient-centered care and prepares you for a broad range of clinical roles.
PGY2 programs allow pharmacists to specialize in fields such as oncology, infectious diseases, or psychiatric pharmacy, offering deeper expertise tailored to advanced practice roles.3 These residencies are ideal for those who wish to concentrate on a specific area of care and pursue board certification or highly specialized roles in clinical pharmacy.

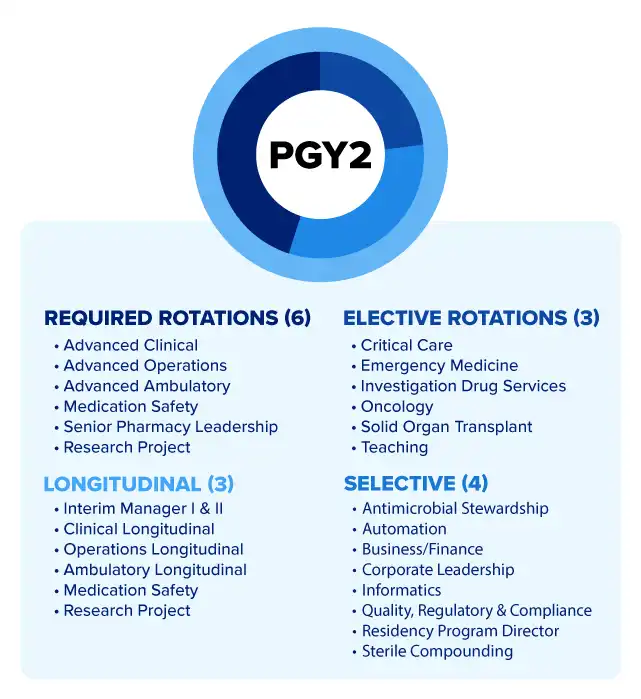
Benefits of Completing a Pharmacy Residency
Completing a pharmacy residency brings invaluable benefits to pharmacists eager to deepen their clinical knowledge and advance their careers. First, a residency hones clinical skills through hands-on training in diverse patient care settings, building competence and confidence. Additionally, residency-trained pharmacists often find expanded career opportunities in specialized or hospital roles that may not be accessible without this training.
Networking is another important benefit. Residency programs connect pharmacists with mentors, preceptors, and other professionals who can offer guidance and open doors throughout their careers.4 These connections often prove invaluable in navigating the field and advancing in specialized practice areas.
How Long is Pharmacy Residency?
Pharmacy residency programs vary in duration, typically lasting 1 to 2 years. PGY1 programs are designed to be completed within 1 year, providing a broad scope of training that prepares you for general practice.
If you choose to pursue additional specialization, PGY2 programs offer a second year of focused training. Some programs may offer combined PGY1 and PGY2 tracks, streamlining the path for pharmacists committed to specialized roles.3 The length of each residency depends largely on the level of expertise desired and the specific requirements of the institution.
Pharmacy Residency Application Process
The pharmacy residency application process is multi-phased, with key deadlines and specific requirements. Applications typically begin in the fall, with deadlines for materials such as a CV, letters of intent, and references occurring in late fall or early winter. Tailoring your application to each program is essential. Highlighting relevant experiences and aligning your goals with the program's strengths can help set you apart.
Additionally, preparing for interviews — often scheduled in early spring — is critical for a successful application.5 Interviewing well demonstrates your readiness and allows you to assess if a program is the right fit. The entire process ensured a match between candidates and programs that best aligns with their professional aspirations.
Pharmacy Residency Programs List
Several top pharmacy residency programs in the U.S. are known for their high-quality training and exceptional mentorship. These programs, including The Johns Hopkins Hospital Pharmacy Residency Program, Mayo Clinic, and the University of Michigan Health System, are recognized for their comprehensive curricula and access to diverse clinical settings. Many reputable institutions provide advanced training, such as the Cleveland Clinic, University of California, San Francisco, and Duke University Hospital.
The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) directory offers a comprehensive list of pharmacy residency programs and helpful insights into each program's unique offerings.6
Pharmacy Residency Match Process
The pharmacy residency match process, managed by the ASHP's National Matching Service (NMS), helps you secure residency placements based on mutual selection.7 Similar to medical residency matching, pharmacy residency applicants submit their preferences, and programs rank applicants in return. The match is competitive, with factors such as experience, recommendation strength, and interview performance impacting match rates.
In recent years, around 82% of applicants have matched to a program, though rates vary across specialties and regions.8 To strengthen your chances, consider building a robust application with relevant clinical experiences and well-written recommendation letters, and prepare thoroughly for interviews to make a lasting impression.
Pharmacy Residency Salary
Pharmacy residents can expect a modest salary, typically ranging from $40,000 to $50,000 annually, depending on the institution and geographic location.9 While residency stipends may seem lower than entry-level pharmacist salaries, the experience gained often leads to higher earning potential in the future.
Factors influencing a resident's salary include the program's funding, location, and additional benefits such as housing stipends or health insurance. Pharmacists who complete residencies often find that the investment in specialized training pays off, as advanced roles in clinical or hospital settings generally offer competitive salaries compared to traditional pharmacy roles.
Getting Started in a Pharmacy Residency
Beginning a pharmacy residency can feel exciting and overwhelming. To set yourself up for success, start by establishing a routine that balances patient care, learning, and self-care. Effective time management will be vital, as will honing your communication skills for interdisciplinary collaboration. Engaging with your preceptors,10 asking questions, and actively participating in clinical discussions will help you get the most out of your learning opportunities.
While a pharmacy residency is challenging, each experience will build the expertise and confidence needed for a successful pharmacy career!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can international pharmacists apply for residency?
What happens after completing a residency?
What are the eligibility requirements for pharmacy residency?
How many pharmacy residency programs should I apply to?
What should I look for in a pharmacy residency program?
References
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. (n.d.). Specialty pharmacy-focused residency programs. Retrieved from https://www.ashp.org/specialty-pharmacy-practitioners/specialty-pharmacy-focused-residency-programs?loginreturnUrl=SSOCheckOnly
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Health system pharmacy administration and leadership residency program structure. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/files/org/locations/akron-general/medical-professionals/graduate-medical-education/hspal-program-structure-2023.pdf?la=en
- Children's Health. (n.d.). PGY1/PGY2 pharmacy residency. Retrieved from https://www.childrens.com/for-healthcare-professionals/education-training/pharmacy-residency/pgy1-pgy2-pharmacy-residency
- Pacific Residency Club. (n.d.). Benefits of a residency. Retrieved from https://www.pacificresidencyclub.com/benefits-of-a-residency
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. (n.d.). Residency application timeline for pharmacy students. Retrieved from https://www.ashp.org/-/media/assets/pharmacy-student/docs/Student-Residency-Guide/psf-residency-application-timeline-Virtual.pdf
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. (n.d.). Residency directory. Retrieved from https://www.ashp.org/professional-development/residency-information/residency-directory?loginreturnUrl=SSOCheckOnly
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. (n.d.). National matching services. Retrieved from https://www.ashp.org/professional-development/residency-information/residency-program-resources/national-matching-services?loginreturnUrl=SSOCheckOnly
- University of North Texas Health Science Center. (2023). HSC College of Pharmacy has historical residency match rate. Retrieved from https://www.unthsc.edu/newsroom/story/hsc-college-of-pharmacy-has-historical-residency-match-rate/
- Salary.com. (n.d.). Pharmacy resident salary. Retrieved from https://www.salary.com/research/salary/posting/pharmacy-resident-salary
- Dalhousie University. (n.d.). What is a preceptor? Retrieved from https://www.dal.ca/faculty/health/practice-education/for-students/what-is-a-preceptor-.html









