NAPLEX stands for the North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination®. It is a high-stakes exam developed by The National Association of Boards of Pharmacy® (NABP®) that pharmacy graduates must take and pass to be licensed to practice pharmacy in the United States. Understanding what is covered on the NAPLEX (or any exam for that matter) is the first step in preparation. NAPLEX content domains provide an outline of testable items.
NAPLEX Content Domains
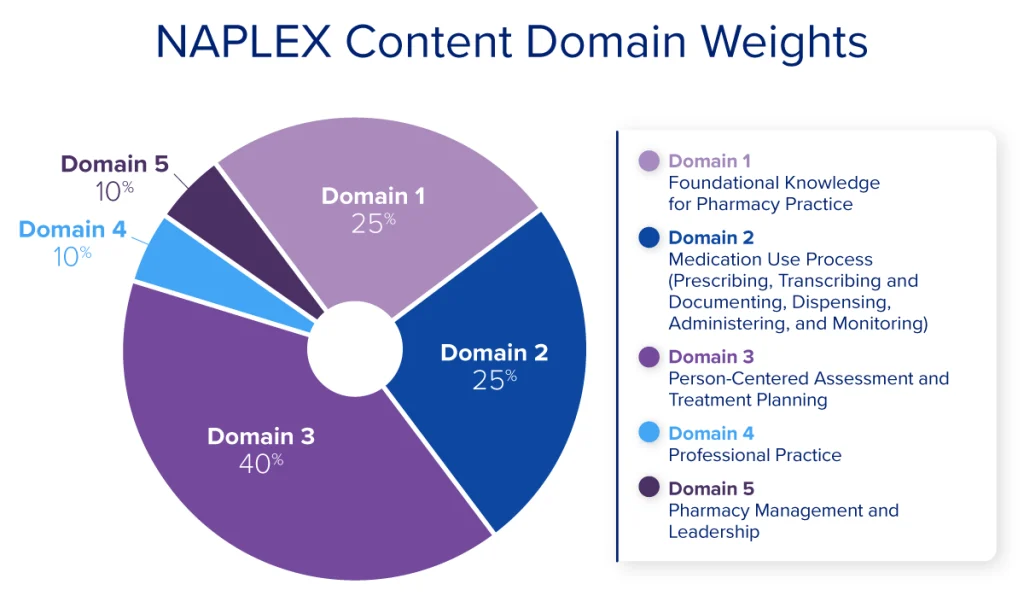
In 2024 NABP announced an update to the NAPLEX blueprint for all exams beginning May 1, 2025. The new NAPLEX Content Outline was developed by practicing pharmacists through a comprehensive analysis of entry-level pharmacy practice. The panel identified essential tasks and the corresponding knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) needed for safe and effective practice. These KSAs were organized into 5 content domains, subdomains, and third-level sub-subdomains. The following table gives you a broad overview of the five content domains tested and the proportion of questions to expect in each area.
| Content Domain | Percentage of Scored Questions | Number of Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Foundational Knowledge for Pharmacy Practice | 25% | 50 |
| Medication Use Process (Prescribing, Transcribing and Documenting, Dispensing, Administering, and Monitoring) | 25% | 50 |
| Person-Centered Assessment and Treatment Planning | 40% | 80 |
| Professional Practice | 5% | 10 |
| Pharmacy Management and Leadership | 5% | 10 |
Domain 1. Foundational Knowledge for Pharmacy Practice
- Pharmaceutical science principles and concepts
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, or pharmacogenomics
- Pharmaceutics
- Pharmaceutical compounding
- Nonsterile preparations
- Sterile preparations
- Pharmaceutical calculations
- Patient parameters or laboratory measures
- Quantities of drugs to be dispensed or administered
- Rates of administration
- Dose conversions
- Drug concentrations, ratio strengths, osmolarity, or osmolality
- Quantities of drugs or ingredients to be compounded
- Nutritional needs and the content of nutrient sources
- Biostatistical, epidemiological, or pharmacoeconomic measures
- Pharmacokinetic parameters
- Drug development processes (eg, clinical trial phases, emergency use authorizations)
- Research design principles and biostatistics (eg, blinding, randomization, biases, statistical tests and outcomes, ethics)
- Retrieval, assessment, and interpretation of primary, secondary, and tertiary resources
Domain 2. Medication Use Process (Prescribing, Transcribing and Documenting, Dispensing, Administering, and Monitoring)
- Prescriptions and medication order interpretation
- Drug names and therapeutic classes
- Indications, usage, and dosing regimens
- Available dosage forms
- Prescription regulations (eg, boxed warnings, risk evaluation and mitigation strategies)
- Safety and effectiveness (eg, laboratory parameters, vital signs)
- Therapeutic substitutions (eg, formulary restrictions, therapeutic alternatives, shortages, biosimilars)
- Immunization services and documentation
- Indications and scheduling
- Contraindications and precautions
- Storage and handling
- Administration (eg, techniques, preparation, routes)
- Adverse reactions
- Medication handling, storage, stability, and disposal (eg, hazardous and nonhazardous drugs, controlled substances, parenteral medications, sharps handling, temperature control)
Domain 3. Person-Centered Assessment and Treatment Planning
- Medication history, allergy history, and reconciliation
- Health histories, screenings, and assessments
- Patient health conditions, including special populations and medication-related factors
- Signs, symptoms, and findings of medical conditions, etiology of diseases, or pathophysiology
- Appropriateness of therapy (eg, medications, immunizations, nondrug therapy, dosing, contraindications, warnings, evidence-based decision making)
- Interactions (eg, drug-drug, drug-condition, drug-food, drug-allergy, drug-laboratory)
- Errors and omissions (eg, dosing, duplication, additional therapy needed, unnecessary therapy)
- Adverse drug reactions
- Toxicologic exposures and overdoses
- Adherence
- Therapeutic monitoring, plan development, evaluation, and modifications
- Therapeutic goals, clinical endpoints, and follow-up
- Safety
- Effectiveness
- Patient education
- Lifestyle modifications and health maintenance
- Medication use, storage, and disposal
- Disease state management
- Over-the-counter medications and dietary supplements
- Devices to administer medications and self-monitoring tests
Domain 4. Professional Practice
- Adverse drug event reporting and medication error reporting (eg, MedWatch, VAERS)
- Public health initiatives and risk-prevention programs (eg, tobacco and nicotine cessation, antimicrobial stewardship, health screenings, opioid stewardship)
- Social determinants and drivers of health
- Ethical considerations (eg, informed consent, ethical principles, professional conduct and responsibility, patient confidentiality)
Domain 5. Pharmacy Management and Leadership
- Pharmacy operations (eg, operational planning, risk management, regulations and regulatory bodies, technology applications and informatics, error-prevention strategies, medication safety)
- Inventory and supply management (eg, drug recalls, drug shortages)
- Quality improvement activities (eg, medication use evaluation, root-cause analysis, continuous quality improvement)
- Mentorship and preceptorship (eg, providing and receiving feedback, delegation of work activities, preceptor roles)
How Content Domains are Tested on the NAPLEX
The NAPLEX content domains provide a general overview of testable content but do not provide specifics on which disease states to study or which formulas to learn. That’s where UWorld RxPrep comes in; we’ve done the work for you. The UWorld RxPrep study materials provide you with the must-know content.
Here is a sample question from the UWorld RxPrep QBank. This question is focused on Domain 3: Person-Centered Assessment and Treatment Planning (specifically 3C2 Appropriateness of Therapy). But look closer… you won’t be able to answer this question correctly without integrating knowledge from other domains.
| Skills required to answer this question and their location in the UWorld RxPrep Course Book | |
|---|---|
|
A 53-year-old female arrives at the emergency department with a severe headache, vomiting, and muscle weakness. She is found to have a right hemisphere hemorrhagic stroke. Past Medical History: hypertension, obesity Vital Signs: BP 185/105 mmHg, HR 110 bpm, RR 24 bpm, O2 sat 90% on room air, T 100.4°F (38°C), Ht 5'9", Wt 130 kg Laboratory Tests: Hemoglobin 12 g/dL Hematocrit 36% Platelets 200,000 cells/mm3 Serum creatinine 1.4 mg/dL What is the best option to prevent a deep vein thrombosis in this patient during the initial period of hospitalization? |
Ability to interpret laboratory values Chapter: Lab Values & Drug Monitoring Knowledge of evidence-based guideline recommendations for treating deep vein thrombosis Chapter: Anticoagulation Ability to calculate creatinine clearance Chapter: Calculations IV - Clinical Knowledge of contraindications and warnings related to anticoagulants Chapter: Anticoagulation |
Use our NAPLEX Study Guide to stay on track and maximize your chances of success.
NAPLEX Content Domain Changes
NABP’s Executive Committee conducts standard-setting exercises every five years to assess the minimum standards for licensure. These exercises may or may not lead to changes in the exam blueprint, but individual exam questions are updated as needed at any time to reflect evolving clinical practice, such as the approval of new medications or updated clinical practice guidelines.
Read More About the NAPLEX
Want to learn more about the NAPLEX? Check out our NAPLEX Exam Guide for everything you need to know, including the registration process and exam format.
Want expert advice to pass the NAPLEX and become a licensed pharmacist? Learn every aspect of NAPLEX exam preparation with our comprehensive study guide.
Want to know everything about how the NAPLEX is scored? Here is an easy-to-follow guide to NAPLEX scoring to help you prepare effectively.
Are you prepared for the NAPLEX? Here is our article with all the details that you will need regarding NAPLEX registration, eligibility, and cost.